Enhanced NER Tagging Model using Relative Positional Encoding Transformer Model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56705/ijodas.v6i2.245Keywords:
Named Entity Recognition, Transformer Model, Relative Positional Encoding, Rule-Based Fine-Tuning, Long-Range Dependencies, Hybrid Architecture, Contextual UnderstandingAbstract
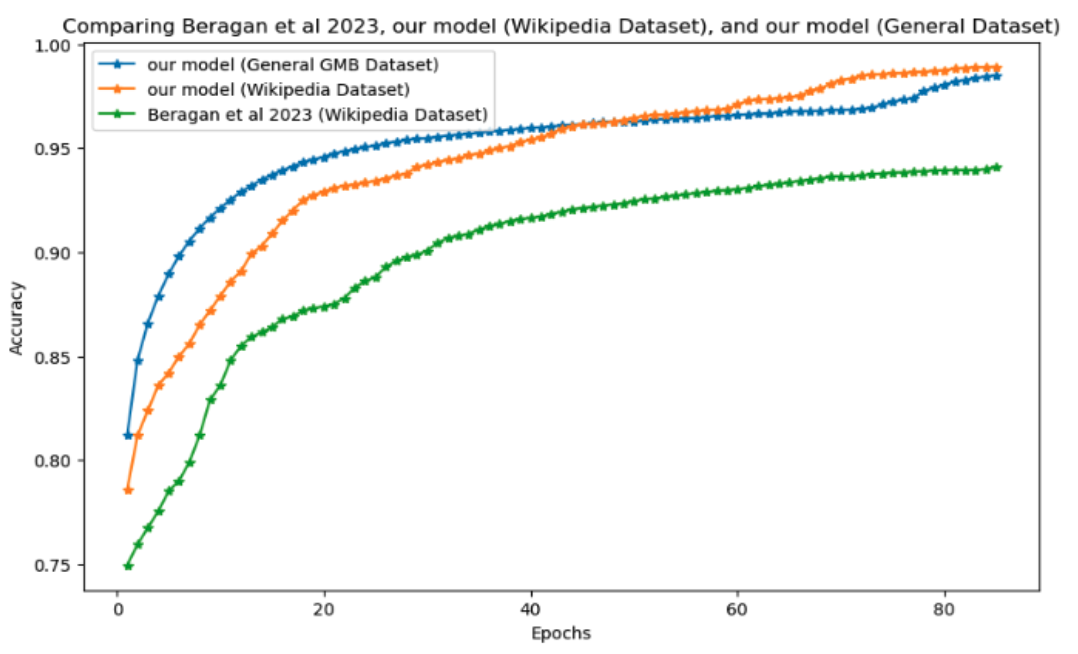
Named Entity Recognition remains pivotal for structuring unstructured text, yet existing models face challenges with long-range dependencies, domain generalisation, and reliance on large, annotated datasets. To address these limitations, this paper introduces a hybrid architecture combining a transformer model enhanced with relative positional encoding and a rule-based refinement module. Relative positional encoding improves contextual understanding by capturing token relationships dynamically, while rule-based post-processing corrects inconsistencies in entity tagging. After being evaluated on the Groningen Meaning Bank and Wikipedia Location datasets, the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance, with validation accuracies of 98.91% for Wikipedia and 98.50% for GMB with rule-based refinement, surpassing existing benchmark research of 94.0%. The relative positional encoding contributes 34.42% to the attention mechanism’s magnitude, underscoring its efficacy in modelling token interactions. Results demonstrate that integrating transformer-based architectures with rule-based corrections significantly enhances entity classification accuracy, particularly in complex and morphologically diverse contexts. This work highlights the potential of hybrid approaches to optimise sequence labelling tasks across domains.
Downloads
References
B. Berragan, A. Singleton, A. Calafiore, and J. Morley, “Transformer-based NER for Geospatial Entities,” 2022.
P. Basile, A. Caputo, and G. Semeraro, “An enhanced Lesk word sense disambiguation algorithm through a distributional semantic model,” in Proc. 24th Int. Conf. Computational Linguistics (COLING), 2014, pp. 1591–1606.
K. Pakhale, “Comprehensive overview of named entity recognition: models, domain-specific applications and challenges,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.14084, Sep. 2023.
Z. Dai, Z. Yang, Y. Yang, J. Carbonell, Q. V. Le, and R. Salakhutdinov, “Transformer-XL: Attentive language models beyond a fixed-length context,” in Proc. 57th Annu. Meeting Assoc. Comput. Linguistics (ACL), 2019, pp. 2978–2988, doi: 10.18653/v1/P19-1285.
P. Shaw, J. Uszkoreit, and A. Vaswani, “Self-attention with relative position representations,” in Proc. 2018 Conf. North American Chapter Assoc. Comput. Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT), 2018, pp. 464–468, doi: 10.18653/v1/N18-2074.
J. Devlin, M. W. Chang, K. Lee, and K. Toutanova, “BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding,” in Proc. 2019 Conf. North American Chapter Assoc. Comput. Linguistics (NAACL-HLT), 2019, pp. 4171–4186, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1810.04805.
B. Y. Lin, C. Tan, Y. Ji, and X. Ren, “RockNER: A simple method to create adversarial examples for evaluating the robustness of named entity recognition models,” in Findings Assoc. Comput. Linguistics: EMNLP, 2021, pp. 3729–3744.
E. T. K. Sang and S. Buchholz, “Introduction to the CONLL-2000 shared task: Chunking,” in Proc. 4th Conf. Comput. Natural Lang. Learning (CONLL/LLL 2000), Lisbon, Portugal, Sep. 2000, pp. 127–132.
Z. Niu, G. Zhong, and H. Yu, “A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning,” Neurocomputing, vol. 452, pp. 48–62, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.091.
S. R. Choi and M. Lee, “Transformer architecture and attention mechanisms in genome data analysis: A comprehensive review,” Biology (Basel), vol. 12, no. 7, p. 1033, Jul. 2023, doi: 10.3390/biology12071033.
N. Patwardhan, S. Marrone, and C. Sansone, “Transformers in the real world: A survey on NLP applications,” Information, vol. 14, no. 4, p. 242, 2023, doi: 10.3390/info14040242.
T. Lin, Y. Wang, X. Liu, and X. Qiu, “A survey of transformers,” AI Open, vol. 3, pp. 1–15, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.aiopen.2022.10.001.
H. Li, H. Mao, and J. Wang, “Part of speech tagging with rule-based data preprocessing and transformer,” Electronics, vol. 11, no. 56, 2022, doi: 10.3390/electronics11010056.
A. Chiche and Y. Yitagesu, “Part of speech tagging: A systematic review of deep learning and machine learning approaches,” J. Big Data, vol. 9, no. 10, 2022, doi: 10.1186/s40537-022-00561-y.
A. M. Rush. The Annotated Transformer. Proceedings of Workshop for NLP Open-Source Software, pages 52–60 Melbourne, Australia, July 20, 2018. c2018 Association for Computational Linguistics
B. Pham, “Parts of speech tagging: Rule-based,” 2020.
S. E. Abdulkareem, M. Abdullahi, and A. E. Evwiekpaefe, “Parts of speech tagging: A review of techniques,” FUDMA J. Sci. (FJS), vol. 4, no. 2, 2020, doi: 10.33003/fjs-2020-0402-325.
G. Lample, M. Ballesteros, S. Subramanian, K. Kawakami, and C. Dyer, “Neural architectures for named entity recognition,” Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguistics, vol. 4, pp. 1–17, 2018, doi: 10.1162/tacl_a_00001.
Y. Liu, W. Li, X. Zheng, and X. Sun, “Adversarial training for low-resource named entity recognition,” in Proc. ACL, 2019, pp. 2171–2181, doi: 10.18653/v1/P19-1210.
A. Akbik, D. Blythe, and R. Vollgraf, “Contextual string embeddings for sequence labelling,” in Proc. 27th Int. Conf. Computational Linguistics (COLING), 2018, pp. 1638–1649.
F. Li, Y. Jin, W. Liu, B. P. S. Rawat, P. Cai, and H. Yu, “Fine-tuning bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) improves biomedical named entity recognition,” Bioinformatics, vol. 36, no. 15, pp. 4236–4242, 2020, doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa375.
H. Lin, Z. Lu, X. Han, and M. Sun, “A multi-task learning framework for cross-domain named entity recognition,” in Proc. AAAI, 2020, pp. 8502–8509, doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i05.6509.
J. A. Achir, M. Abdulkareem, and M. Abdullahi, “Improving part-of-speech tagging with relative positional encoding in transformer models and basic rules,” Indonesian J. Data Sci., vol. 6, no. 1, 2025, doi: 10.56705/ijodas.v6i2.184.
P. Basile, J. Bos, K. Evang, and N. Venhuizen, “Groningen meaning bank,” 2012.
S. A. Hicks, I. Strümke, V. Thambawita, M. Hammou, M. A. Riegler, P. Halvorsen, and S. Parasa, “On evaluation metrics for medical applications of artificial intelligence,” Sci. Rep., vol. 12, no. 1, 2022, doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09954-8.
C. D. Manning, P. Raghavan, and H. Schütze, Introduction to Information Retrieval. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2008, doi: 10.1017/CBO9780511809071.
X. Li, L. Mao, and Y. Wang, “Contextual token classification via relative positioning,” 2022.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain copyright and full publishing rights to their articles. Upon acceptance, authors grant Indonesian Journal of Data and Science a non-exclusive license to publish the work and to identify itself as the original publisher.
Self-archiving. Authors may deposit the submitted version, accepted manuscript, and version of record in institutional or subject repositories, with citation to the published article and a link to the version of record on the journal website.
Commercial permissions. Uses intended for commercial advantage or monetary compensation are not permitted under CC BY-NC 4.0. For permissions, contact the editorial office at ijodas.journal@gmail.com.
Legacy notice. Some earlier PDFs may display “Copyright © [Journal Name]” or only a CC BY-NC logo without the full license text. To ensure clarity, the authors maintain copyright, and all articles are distributed under CC BY-NC 4.0. Where any discrepancy exists, this policy and the article landing-page license statement prevail.














